Building Grenada’s Strategic Framework to Enhance the Country’s Capacity to Transition to Low Emission Development
Building Grenada’s Strategic Framework to Enhance the Country’s Capacity to Transition to Low Emission Development
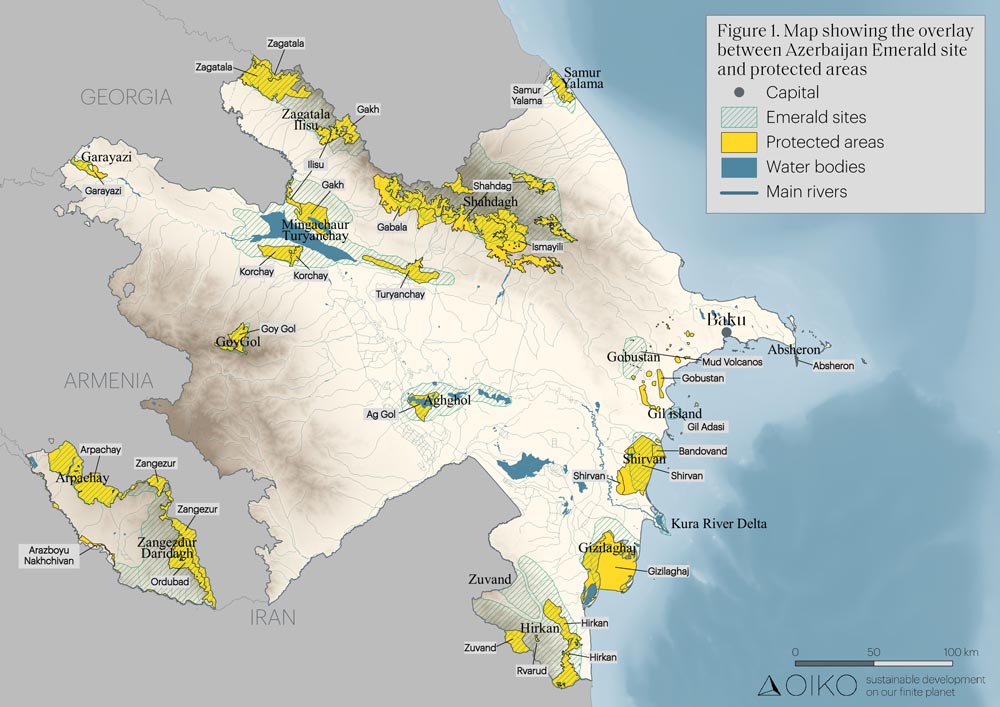
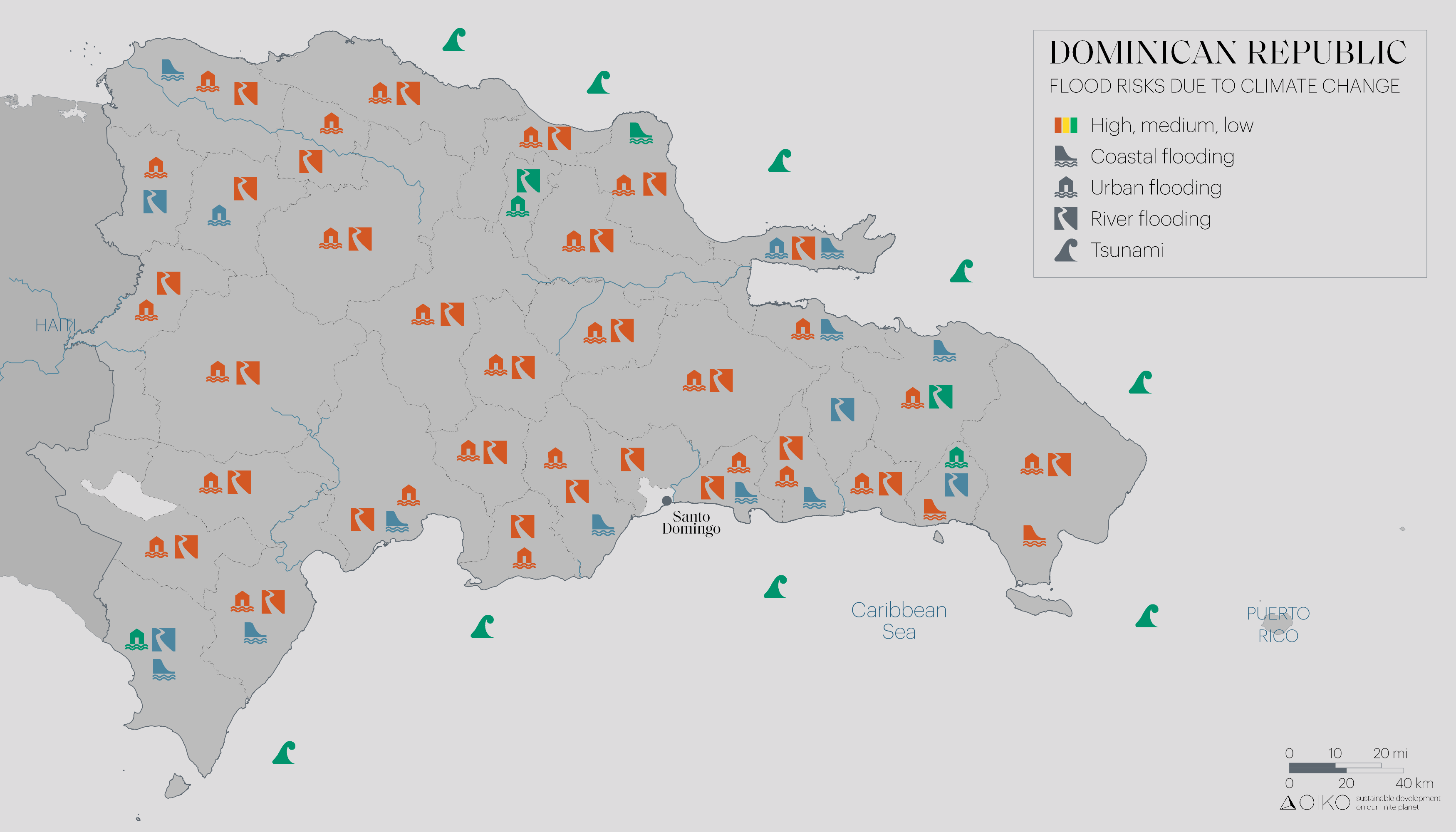
The aim of the project is to catalyze a significant change in approach do that Grenada can transition towards a development path with lower emissions. This transition involves creating a plan called the Low Emission Development Strategy and Action (LEDSA) Plan. By making this shift, Grenada aims to decrease its greenhouse gas emissions and fulfill its commitments outlined in its NDCs and Energy Policy. The assignment focuses on Grenada’s efforts to develop and strengthen its strategic frameworks. These frameworks aim to tackle policy gaps, enhance sectoral expertise, and create supportive environments for Green Climate Fund (GCF) programming, particularly in low-emission investments.
This endeavor will primarily result in the creation of the Low Emission Development Strategy and Action (LEDSA) as a crucial national document. The LEDSA will serve es a guide for Grenada’s transition towards low-emission development.
This task directly contributes to two outputs of the GRD-RS-007 project:
- Identifying business opportunities and stimulating interest and innovative investments in various sectors such as Power, Transport, Agriculture, Hotel and Commercial, Manufacturing, and Household. The private sector’s role is emphasized to determine how their investments can be effectively integrated nationally to bolster financing and support Grenada’s Low Emission Development (LED) GOALS.
- Develop a Resource Mobilization Strategy for Grenada’s Low Emission Development Strategy and Action (LEDSA). This strategy will provide a clear direction of accessing climate financing from a range of sources including national, regional, and international entities, as well as through bilateral and multilateral partnerships. These funds will be instrumental in financing the implementation of low-mitigation options and investment opportunities outlined in the LEDSA.
Description of actual services provided by your staff within the assignment:
- Stakeholder consultations and engagement
Pre and post effectiveness surveys
Formulation of a Sectoral Business Opportunities Report
Resource Mobilization Strategy
Capacity Building and Workshop
COUNTRY
GRENADA
IMPLEMENTATION PERIOD
2024 · Ongoing
DONOR · PARTNER
Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre (CCCCC)